The Ethics of UGC: Balancing User Rights and Brand Promotion
Meta Description: Navigating the complexities of user-generated content (UGC) is essential for brands wanting to ethically promote their products while respecting user rights. Discover key considerations and best practices.
User-generated content (UGC) has transformed the landscape of digital marketing as brands increasingly seek engagement through authentic consumer interactions. However, with this empowerment comes the important responsibility of understanding the ethical dimensions of using such content. In this blog, we delve into the ethics of UGC, focusing on the delicate balance between respecting user rights and promoting brand interests.
My name is Lukas Baran, and I have over five years of experience in SEO and content strategy, guiding numerous businesses in enhancing their digital presence. In this post, we will explore the legal and ethical considerations of UGC, supported by relevant data and real-world examples.
Understanding User-Generated Content (UGC)
Definition of UGC
User-generated content refers to any content—such as text, videos, images, and reviews—created by users rather than brands. Common platforms for UGC include social media sites like Instagram, TikTok, and Yelp, where consumers actively share their experiences and opinions about products and services.

The Rise of UGC in Marketing
The popularity of UGC stems from its perceived authenticity, which significantly influences consumer behavior. According to a study by Nielsen, 92% of consumers trust organic user-generated content over traditional advertising. As such, brands are increasingly leveraging UGC to foster engagement and loyalty. However, this growing trend necessitates awareness of rights and ethical considerations associated with using this content.
Legal Frameworks Surrounding UGC
Navigating the legal landscape surrounding UGC can be complex, necessitating an understanding of several key frameworks:
Copyright Law
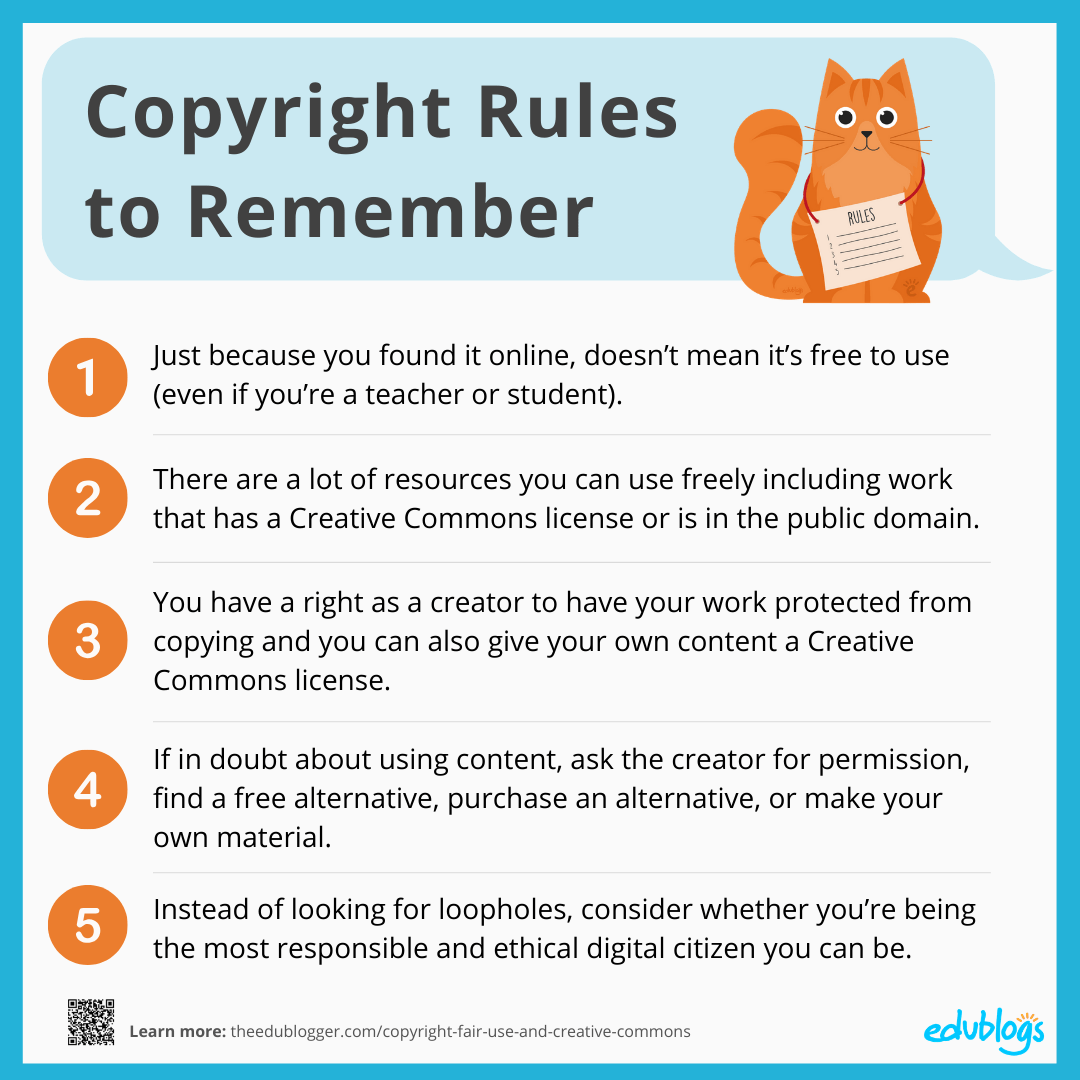
Under copyright law, original creators retain rights to their work. This principle means brands must ensure they have the appropriate permissions to use UGC. For instance, the U.S. Copyright Office states that both visual and written content is protected, and using it without consent can lead to legal repercussions.
Fair Use Doctrine
Fair use allows for limited use of copyrighted material without permission under specific circumstances. Brands must tread carefully, as the boundaries of fair use vary by case. The landmark case Campbell v. Acuff-Rose Music, Inc. established important precedents around transformative use, yet relying on fair use as a blanket justification can be risky for brands.
GDPR and Privacy Regulations
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has significant implications for UGC, especially concerning user consent and data protection. Brands operating in or targeting European consumers must ensure they comply with GDPR standards, obtaining explicit consent before using user content.
The Importance of User Rights
Educating brands and consumers about user rights is essential in establishing a sense of respect and responsibility around UGC. Here's why safeguarding user rights matters:
Advocating for Fair Treatment
Brands should not only seek permission to use UGC but also recognize the contributions of users. Acknowledging the creators behind the content can foster trust and respect between brands and their audience.
Practical Steps to Protect User Interests
Always Ask for Permission: Obtain explicit consent from users before using any of their content. This demonstrates respect and can lead to a more positive relationship.
Attribution: Credit users by tagging them or mentioning their names when sharing their content. This kind of recognition can encourage users to engage willingly with brands in the future.
Transparent Terms: Clearly outline how user content will be used in the terms of service, ensuring users feel secure about their contributions.
Building Trust Through Ethical UGC Practices
Brands that prioritize ethics when utilizing UGC can enhance their reputation and foster loyalty among consumers. Here are some effective strategies:
Successful Brand Examples
Coca-Cola: The "Share a Coke" campaign encouraged customers to share images of personalized Coke bottles on social media, capitalizing on the authenticity of user-generated posts. Coca-Cola sought permission before featuring user content and thanked contributors, creating a powerful connection with their audience.
Starbucks: By running social media contests that invite customers to share images of their favorite drinks, Starbucks effectively encourages UGC while promoting their brand. They ensure that submissions are used with permission, contributing to a sense of community among their customers.
Learning from Ethical Failures
Brands that misuse UGC can suffer substantial backlash. For example, Jones Soda faced criticism for utilizing customer photos without permission, damaging their reputation. Understanding the ramifications of unethical practices can guide brands toward more responsible marketing strategies.
Best Practices for Ethical UGC Handling
To navigate the ethical landscape of UGC, brands can implement several best practices:
Create UGC Submission Policies
A well-defined UGC submission policy communicates guidelines that respect user rights while encouraging contributions. This transparency fosters a culture of collaboration instead of exploitation.
Encourage Engagement and Feedback
Brands should actively engage with users, encouraging dialogue about how their content is shared. This practice cultivates a sense of involvement and respect.
Emerging Trends Shaping UGC Ethics
As technology evolves, so do ethical considerations surrounding UGC. Notable trends in this area include:
Blockchain for Image Rights Management

Blockchain technology offers capabilities for digital rights management, verifying content ownership and usage rights straightforwardly. This innovation can protect both creators and brands while simplifying the process of obtaining permissions.
AI Tools for Automating Permissions
AI solutions are emerging to aid brands in obtaining permissions and tracking content attribution. By integrating these tools, brands can streamline ethical practices while minimizing the risk of infringing user rights.
Conclusion
Navigating the ethics of user-generated content is crucial for brands seeking to develop meaningful relationships with consumers. By emphasizing ethical engagement and respecting user rights, brands can foster trust, loyalty, and authenticity in their marketing efforts. As UGC continues to shape the digital marketing landscape, prioritizing ethical considerations will not only enhance brand reputation but also promote responsible marketing practices.
For those interested in delving deeper into the ethics of UGC and exploring actionable strategies, consider subscribing to our newsletter for further insights and resources designed to elevate your digital marketing efforts.
